Gone are the days when the idea of 3D printed jewelry sounded like a sci-fi movie. A growing number of designers are 3D printing their designs these days and there is no discernible difference between a piece of printed jewelry and one manufactured by traditional methods. 3D printed jewelry is about to become the norm. Let’s see why.
Which 3D printing technologies are the most widely used in the jewelry industry?
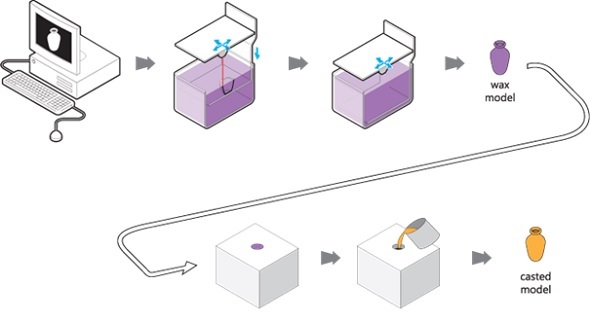
The wax casting procedure is commonly used in the creation of gold, silver, bronze and brass jewelry. It draws both on modern 3D printing technology and traditional molten metal work.
It all begins with the printing of a 3D model in a wax-like resin or other castable material. One or more sprues are attached to this model which is then attached to a wax ‘tree’, together with a number of other models. The tree is then placed in a flask and covered in a fine plaster. When the plaster solidifies, it forms the mold for casting the metal. The plaster mold is then heated in an oven for several hours until the wax is completely burned out.
What are the advantages of this technology?
The above combination of 3D printing and traditional jewel craft techniques is, to date, the most efficient and economic way to produce 3D printed jewelry. It results in a true solid finish, smooth surfaced or otherwise, depending on the taste of the designer, and is also suitable for hand finishing.
- Its greatest advantage is that it eases jewelry designers’ production-side concerns. Once generated, the digital file contains all the information that is required for printing.
- Another major advantage is that the 3D files are so easy to edit. In a single day you can print as many prototypes of the 3D model as you like, with all the tweaks and interactions required to obtain optimum results. Of course, this is only possible if there’s a 3D printer right there in the jeweler’s workshop
- Lastly, SLA printing resolution provides a level of detail that would be practically impossible using traditional methods.
What materials and finishes are used in 3D jewelry printing?
Designers mainly use metals to which they can apply a variety of finishes:
- Brass: gold-plated, color-plated, PU coated
- Silver: with gloss, high gloss, satin, sand-blasted or antique finish
- Gold: 14k or 18k
- Bronze: PU coated, polished
As well as metals, jewelry designers also use other 3D printable materials such as polyamide (derived from nylon), alumide (a mix of polyamide with aluminum powder), rubber-like materials and even ceramics.
Whatever happened to the human touch?
Despite all this talk of 3D printers and state-of-the-art technology, the human touch remains ever present and still plays the key role in the jewelry-making process.
- The designer uses 3D or CAD modelling software to create the design, which therefore reflects a truly personal inspiration and style. Nothing can replace the talent and eye of the creator.
- From printing to post-processing, the human hand is always present. So the human element is still a very important part of a design’s success.



